openpilot is an open source driver assistance system. openpilot performs the functions of Automated Lane Centering and Adaptive Cruise Control for over 200 supported car makes and models.
You can not select more than 25 topicsTopics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
| Geodetic | [Latitude, Longitude, Altitude] | geodetic coordinates | Sometimes used as [lon, lat, alt], avoid this frame. |
| ECEF | [x, y, z] | meters | We use **ITRF14 (IGS14)**, NOT NAD83. <br> This is the global Mesh3D frame. |
| NED | [North, East, Down] | meters | Relative to earth's surface, useful for vizualizing. |
| Device | [Forward, Right, Down] | meters | This is the Mesh3D local frame. <br> Relative to camera, **not imu.**<br> 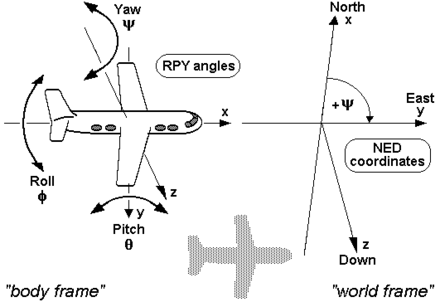|
| Road | [Forward, Left, Up] | meters | On the road plane aligned to the vehicle. <br>  |
| View | [Right, Down, Forward] | meters | Like device frame, but according to camera conventions. |
| Camera | [u, v, focal] | pixels | Like view frame, but 2d on the camera image.|
| Normalized Camera | [u / focal, v / focal, 1] | / | |
| Model | [u, v, focal] | pixels | The sampled rectangle of the full camera frame the model uses. |
| Normalized Model | [u / focal, v / focal, 1] | / | |
Device frame is aligned with the road-facing camera used by openpilot. However, when controlling the vehicle it makes more sense to think in a reference frame aligned with the vehicle. These two reference frames are not necessarily aligned. Calibration is defined as the roll, pitch and yaw angles that describe the orientation of the vehicle in device frame. The vehicle orientation is the orientation of the vehicles's body, the orientation of the vehicle can change relative to the road because of suspension movements.
The roll of the vehicle is defined to be 0 when the vehicle is on a flat road and not turning. Pitch and yaw are defined as the angles that describe the direction in which the vehicle travels when it is driving on a flat road and not turning.
It is important for openpilot's driving model to take in images that look as if the calibration angles were all zero. To achieve this the images input into the model are transformed with the estimated calibration angles. At the moment, roll calibration is always estimated to be zero.